Every once in a while, you hear about a set of identical twins that’s marrying another set of siblings. Usually, they make the news because they are going to have a double wedding and it’s a big deal.
Many people will say it’s kind of weird that they’re marrying siblings. But if the couples aren’t genetically related, there’s no harm.
Perhaps it creates one of the more interesting family trees, though.
So, when two families like this decide it’s time to have children, what would the relationship between the first cousins be?
A unique circumstance like this one actually has a term, double first cousins.
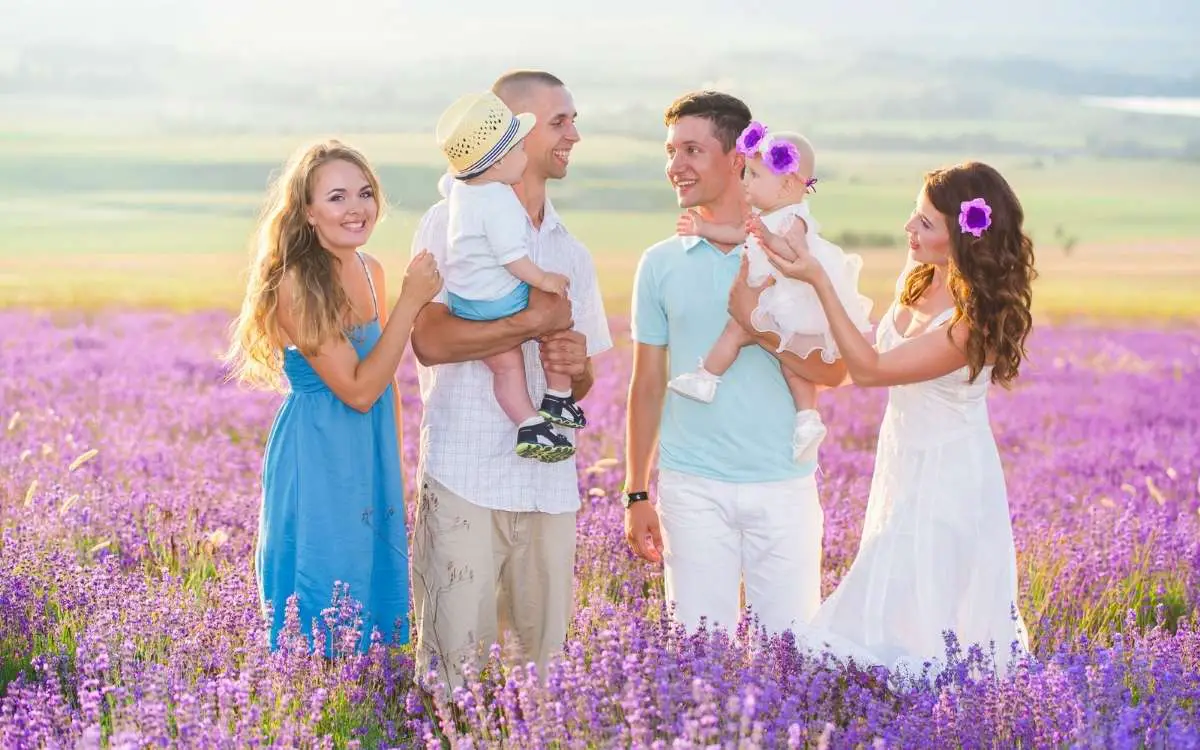

Family History of Two Sisters and Two Brothers
You might also hear it associated with the phrase “cousins on both sides” because they are basically doubly related.
Talk about complicated relationships.
This first cousin relationship is unlike others due to the closely related parents. Most children have parents who are not related to the parents of their cousin by more than one parent.
So, instead of having four separate sets of grandparents, there are four grandparents in total.
Having the same amount in common between cousins might cause annoyance. Kids can be kids, after all.
If the gene pool has lessened by that much, what would that mean for the double first cousin DNA profile in the genealogy world?
How Much DNA Do Double Cousins Share?
Technically, are double cousins genetically siblings? Double first cousins are closer than typical first cousins.
Effectively, double cousins share 25% of DNA, in comparison with most first cousins who share 12.5%.
That’s twice as much DNA for double first cousins.
For anyone analyzing the numbers, that means double first cousins are as closely related as half-siblings or grandparents.
That makes finding a common ancestor or several genealogy links that much easier.
Another thing about the DNA that double first cousins share is that if both their parents were identical twins, only one cousin would need to take a DNA test.
The reason is that identical twins pretty much inherit the same DNA from their parents.
What if two sets of identical twins, two sisters, reproduced with another set of identical twins, two brothers?
That would make their children genetically more like full siblings rather than first cousins.
The double first cousin relationship really narrows the family tree, on that branch anyway.
How Rare Are Double First Cousins?
Double first cousins are quite rare, especially in modern times. The reality of this day and age in comparison with times of the past is our ability to stretch out.
People go far and wide for a number of reasons and find mates elsewhere.
Twice as Related
Double first cousins are two times as related as most cousins. Sharing all the grandparents and all the ancestors.
A double first cousin is basically one family with the other.
The likelihood of finding a mate that is the sibling of your sibling’s mate is a one-in-a-million chance. It was certainly more likely a century ago or prior.
Today, it might happen in smaller towns where close family ties are part of the local community.
What Is a Double Cousin Marriage?
Before double first cousins arise, double-cousin marriages often proceed.
As you might have guessed, the example mentioned earlier was exactly what a double-cousin marriage is; two siblings marrying two siblings from another family.
What about more complicated topics related to common ancestors, like double second cousins? That’s when one double first cousin has a child followed by another child from the other double first cousin.
The offspring of a pair of double first cousins are double second cousins. These cousins share DNA that is from a tight pool.
Calling that a mouthful is putting it lightly.
Can Double First Cousins Marry?

In 24 states across the US, it is illegal for first cousins to marry. That means there are 22 states where it is legal and six more where it’s only legal in very specific situations.
Double first cousins though? It would seem that even in those 22 legal states, the family or the court would have the right to step in and say something about it.
Double cousins share too much DNA for that to be legally binding.
As noted previously, it would be like half-siblings getting married and there is no state where siblings can marry, half-sibling or not.
What Happens When First Cousins Procreate?
The main reason why it is a legal issue for double first cousins or a regular first cousin to marry boils down to genetics. Birth defects increase the closer the relationship between two parents.
To be fair, if this is the first time in at least a very long time that a first cousin couple has reproduced, the children will probably be healthy.
Not saying the other cousins and family will be okay with it, but that’s another matter.
Historical Inbreeding
The real problems start to develop within a family tree when inbreeding happens repeatedly throughout generations.
There’s no better real-life example than the royal families throughout Europe.
Overlap wasn’t a thought for centuries. Royal houses wanted to keep power within the family, therefore marrying relatives was commonplace.
Ancient Power Struggles
Not to specifically point out Europeans, ancient Egyptians had no problem with the practice either. A king and queen could possibly have at least one of the same parent.
Children were put into those positions at a young age and were made to marry siblings who share the same amount of DNA.
Hapsburg Jaw
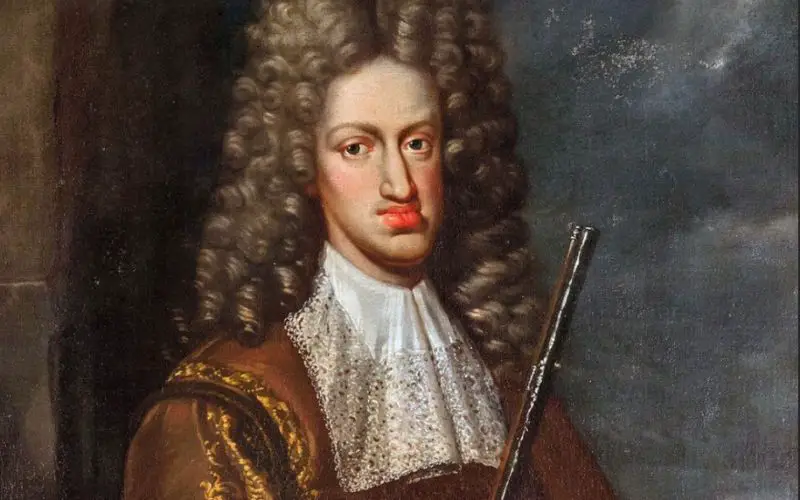

It didn’t occur to anyone until much later that there could be problems with intermarrying within the same generation or two. When new DNA isn’t introduced within a family line, deformities begin to show up.
Over time, these mutations begin to have a major impact on the health and stability of an individual. A noticeable example that can be traced all over Europe is the Hapsburg Jaw.
This facial deformity was basically an elongated lower jaw. Many royals back in the day had some form of it, from just barely to undeniable.
Unfortunately, King Charles II of Spain had it the worst. Luckily, he was unable to provide the kingdom with any heirs. Charles had a multitude of issues brought on by consistent inbreeding over generations.
According to All That Interesting, “In addition to his Habsburg jaw, the king was short, weak, impotent, mentally handicapped, suffered numerous intestinal problems, and did not even speak until he was four years old. ”
Let’s not forget that it was said of Charles that he was so ugly it caused fear. If that’s not a reason to introduce new blood to the gene pool, nothing is.
Genetically Related Matches
If double first cousins would be a no-go romantically, what about a second cousin or third cousin?
While the waters get more diluted the farther out you get, it’s important to remember that all cousins shared ancestors.
A second cousin shares the same great grandparents. A third cousin shares great-great-grandparents.
The sets of grandparents shared might be a bit much even for the third cousin, depending on how close the family is.
A genetic relationship at any distance can create some interesting family histories.